Being an engineer is not easy, but we can make you a real one.
Civil Engineering
Study civil engineering to become a real professional in the field by studying civil engineering in 4 sub-branches to become a real leader in civil engineering and construction management, including structural engineering, construction management, geotechnical engineering, water resources engineering or irrigation engineering, transportation engineering, surveying engineering, environmental engineering, etc.
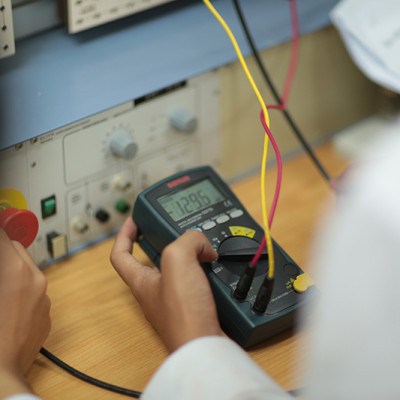
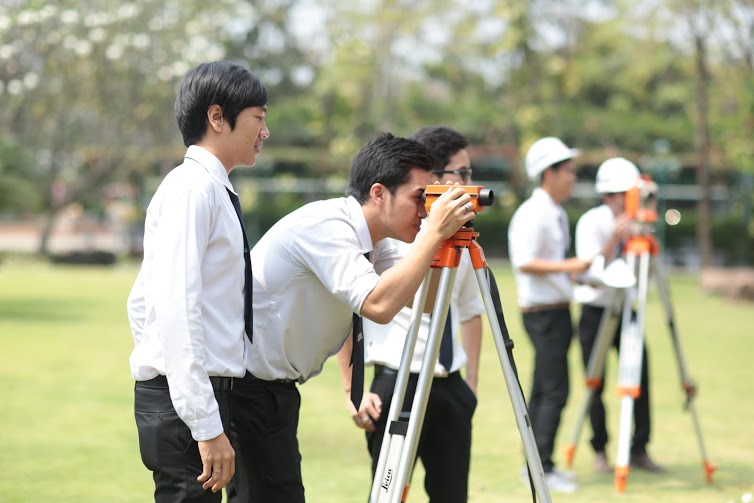




Branch Highlights
“The real deal in civil engineering!”
Studying civil engineering at Sripatum University will push students to become top-notch civil engineers because it provides more in-depth knowledge than anywhere else. Discover the Gointer program, study in Thailand for 2 years and then study in Australia for another 2 years, providing both civil engineering knowledge and language skills for career advancement. During the civil engineering study, there are expert lecturers who closely supervise students, providing full civil engineering skills, along with a project to develop students’ potential so that they have the potential to compete with engineers who graduated from other institutions. The program is certified by the Engineering Council. Upon completion, students can apply for a license to practice as a controlled engineer (กว.).
Course Description>> Attachments Course Description for the 2012-2016 Curriculum
Department tuition fees
First semester fee
Civil Engineering-
Term 1 / 35,900.-
Loan Fund
Civil Engineering-
High school graduate/Vocational Certificate/NFE graduate
-
Regular semester
Registration Payment
Option 1: Pay by borrowing from the Student Loan Fund, starting at only 4,000 baht. The rest is borrowed from the Student Loan Fund.
Option 2: Pay in full by yourself
Option 3: Pay a portion of 15,000 baht yourself and pay the remaining amount by the date specified by the university.


Course Structure

What do civil engineering students study?
Department of Structural Engineering
Analyze, design, select the type of structure and the appropriate materials to make the building structure able to withstand the weight strongly and safely, control the construction work to be in accordance with the standards, regulations and design, as well as study and develop the properties of materials appropriate for the construction work. The nature of work in the field of structural engineering can be divided into reinforced concrete work, steel structure work and prestressed concrete work. Currently, some knowledge has separated from the field of structural engineering, such as bridge engineering, which does bridge design and construction as the main work, and earthquake engineering, which studies the analysis of earthquake waves, and the design of structures that can withstand forces from earthquakes.
Construction Management Branch
The construction management branch is responsible for managing, planning the implementation and use of resources, tools, and people in construction work to be efficient, fast, and economically worthwhile, as well as construction techniques and project readiness. The positions of engineers who work in this branch include project managers and project engineers, who are usually engineers who come from construction control fields. After working for a certain period of time, they will be assigned to oversee administrative work.
Soil Engineering (Geotechnical Engineering)
Work in this field involves analyzing the bearing capacity of soil structures, designing piles, retaining walls, solving problems in soft soils, improving soil quality, stabilizing soils, designing various underground structures and finding construction methods suitable for soil conditions.
Water Resource Engineering
Water resources engineering is a branch that arises when the demand for water as a factor for living increases and sometimes there is a shortage of natural water. Therefore, water resources must be managed to distribute to communities equally. Water resources engineering plays this role. Subjects in water resources engineering consist of hydraulics applied together with hydrology. Students who wish to study in this branch must be able to analyze the issues and solve them by using appropriate water resources management technology. This is a factor to promote the development of the agricultural sector, housing, community physiology, and industrial development under the form of self-reliance, while also participating in supporting other branches of engineering. The obvious characteristics of the work include reservoirs, dams, spillways, water gates, water outlet buildings, water flow in waterways, pressure pipes, water turbines, water pumps, drainage, and flood prevention systems.
Transportation Engineering
Nowadays, transportation plays a very important role in our daily lives. It can be said that if there is no good transportation, the country will not develop. This is because transportation is a part of transportation that aims to move things, people or animals to other points by land, water, air and transportation systems (e.g. pipes). The duties of transportation engineering are planning, studying the feasibility of projects, studying the needs of transportation and travel, designing transportation systems to be convenient, fast, safe and economically worthwhile. Examples of work in the field of transportation engineering
There is also a related branch, which is road engineering. Road engineering is a branch that deals with designing routes for land transportation, especially roads. It is a branch that has been around for a long time since the demand for cars increased. The duties of road engineering include laying out road networks to provide maximum access to areas and to facilitate travel, laying out routes and designing road geometric features to be consistent with topography and economic conditions, overseeing road construction, selecting road materials, maintaining them, and laying out traffic signs and travel information. Agencies in the country that are involved in road construction include the Department of Highways, the Department of Public Works, the Office of Accelerated Rural Development, Bangkok, and various municipal offices, etc.
Survey Engineering
Surveying engineering focuses on planning both horizontal and vertical terrain for construction work in wide areas. The purpose is to determine the correct location. Surveying engineering works are involved in many fields and are in the early stages of the project. Examples of surveying engineering works include surveying for mapping, road layout, surveying for vertical alignment of buildings, satellite surveying, etc.
Environmental Engineering
Formerly known as Sanitary Engineering, this branch of study was born from the deterioration of the world’s environment from industrial and technological advancements, which has caused many problems such as wastewater, waste, and air pollution. These problems are being given great importance by local, national, and international organizations. Environmental laws and standards have been increasingly enforced both domestically and internationally. The work of environmental engineering aims to manage and control work processes and production to minimize pollution, design and install pollution control systems. Examples of work in this branch include construction of wastewater collection and treatment systems, waste collection and disposal systems, filtration and water delivery systems, etc.
Course Structure
The number of credits studied throughout the course is not less than 151 credits.
Course No. | Credits |
|---|---|
1. General studies subjects | 30 credits |
1.1 Humanities and Social Sciences Group | 9 credits |
1.2 Language and Communication Studies Group | 14 credits |
1.3 Mathematics and Science subject group | 7 credits |
2. Specialized subjects | 115 credits |
2.1 Basic vocational subjects group | 35 credits |
2.2 Compulsory subjects | 62 credits |
2.3 Elective subjects | 18 credits |
3. Elective subjects | 6 credits |
>>Curriculum Plan/Curriculum Structure<<
Degree Name
- Thai (full name): Bachelor of Engineering (Civil Engineering)
- (Abbreviation) : B.Eng. (Civil Engineering)
- English (Full name): Bachelor of Engineering (Civil Engineering)
- (Abbreviation) : B.Eng (Civil Engineering)
Duration of study, course
4-year course (regular program)
Study during office hours, Monday – Friday, 9:00 a.m. – 5:00 p.m.
4-year course (part-time)
Study outside of office hours, Saturday – Sunday, 9:00 a.m. – 5:00 p.m.
CAREER PATH
Civil Engineering
 Structural engineering
Structural engineering Construction management
Construction management Soil engineering (or geotechnical engineering)
Soil engineering (or geotechnical engineering) Water resource engineering
Water resource engineering
or irrigation engineering Transportation engineering
Transportation engineering Survey engineering
Survey engineering Environmental engineering
Environmental engineering
Leading companies that DEK-SPU can choose!
 Ministry of Transport
Ministry of Transport Ministry of Interior
Ministry of Interior Construction Contractor
Construction Contractor Consulting and design company
Consulting and design company Real estate development company
Real estate development company Technical service companies or agencies
Technical service companies or agencies Department of Public Works and Town & Country Planning, Department of Highways, Department of Lands
Department of Public Works and Town & Country Planning, Department of Highways, Department of Lands Department of Rural Roads, Royal Irrigation Department, Department of Water Resources
Department of Rural Roads, Royal Irrigation Department, Department of Water Resources Local government agencies: Subdistrict Administrative Organizations (SAOs), Provincial Administrative Organizations (PAOs), and Municipalities
Local government agencies: Subdistrict Administrative Organizations (SAOs), Provincial Administrative Organizations (PAOs), and Municipalities  Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand, Provincial Electricity Authority
Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand, Provincial Electricity Authority
Metropolitan Electricity Authority, Waterworks Authority, PTT Such as sales support work, related testing services
Such as sales support work, related testing services
Faculty



Review
New things, highlights, differences
Faculty of Engineering, Sripatum University guarantees the quality of success with more than half a century of teaching experience under the concept of “Simply Significant”, an important force driving towards success with cooperation from professional engineering professors who are ready to be an important force in pushing the potential of students to succeed by allowing students to study engineering with deep knowledge! Real knowledge! Real practice! Through the most modern tools and laboratories.
Scholarship
SPU quota scholarship
Good scholarships that don't use TCAS scores No interview, no portfolio submission required
SPU Portfolio 3 Good Scholarship
Port collector line Receive up to 40,000 baht in funding*
Real SPU scholarship
Apply and submit a portfolio 100% free study*







